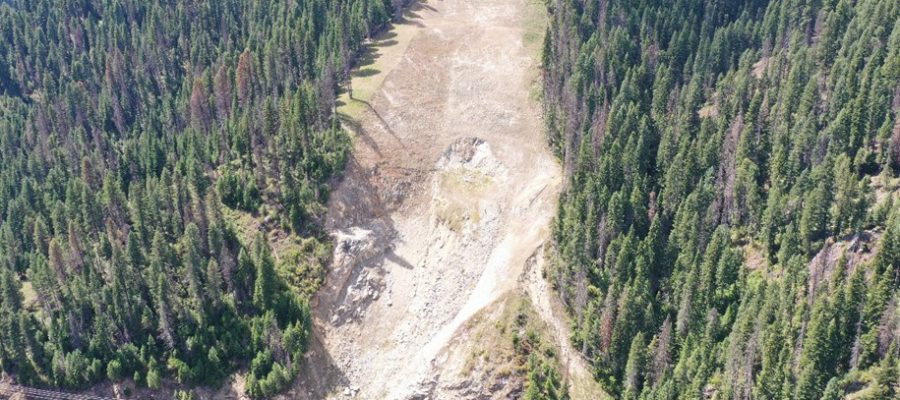
The Idaho Geological Survey (IGS) is helping the Idaho Transportation Department (ITD) learn more from landslides in the Gem State. A new statewide inventory database of landslide and rock fall hazards released by IGS in late June will assist ITD, emergency managers, and planners with forecasting and hazard mitigation by identifying problematic hot spots.
The project was sponsored by ITD’s Division of Highways – Construction and Materials team and funded through ITD’s Research Program.
The inventory contains more than 2,400 landslide entries spanning from prehistoric to active events. It’s posted on the IGS website and can be accessed through an interactive webmap service.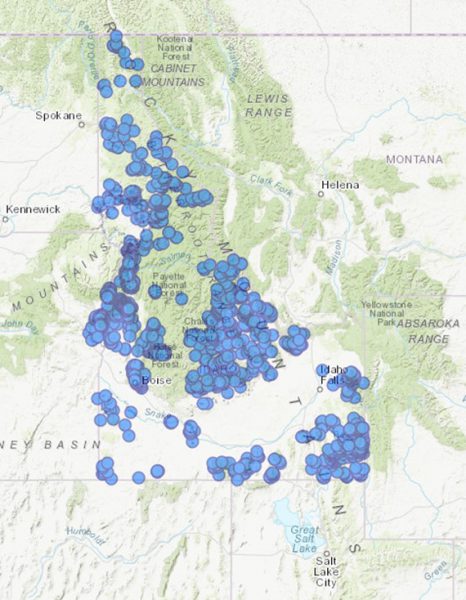
The information was also added to ITD’s IPLAN online ArcGIS platform. The database includes attributes to maintain MSE retaining wall locations and risk factors to evaluate the condition of the wall, as well as attributes for rock fall risk, so ITD districts can assess the problematic areas that could cause road closures.
Data were compiled from historic archives, information provided by ITD geotechnical staff and district geologists, unpublished IGS field observations, analysis of LiDAR imagery, remote sensing, satellite images, and newly mapped landslides.
“The study represents a live catalog of mass movements across the state with a particular focus on transportation corridors and urban areas,” said State Geologist and IGS Director Claudio Berti. “The database is a tool for documenting and assessing slope stability hazards. It is not intended to predict future events, but to document known events and show broad patterns of occurrence.”
This new database replaces the last inventory published in 1991, a static map no longer suitable for modern digital analyses. The 2021 version will be kept up to date as new events occur or new information becomes available.
Landslide problem areas in Idaho include: Bonners Ferry, Clearwater River Basin, Horseshoe Bend, Boise Foothills, Hagerman, U.S. 95 between Pollock and Lucile, and U.S. 26 between Swan Valley and the Wyoming border. Geologic characteristics of the bedrock, fractures, systems, precipitation, regional hydrogeology, vegetation, wildfires, and steepness of hillslopes are all contributing factors in landslide initiation and development.
You can also learn more by reading the full research report linked here.

